Multi-Session Operation
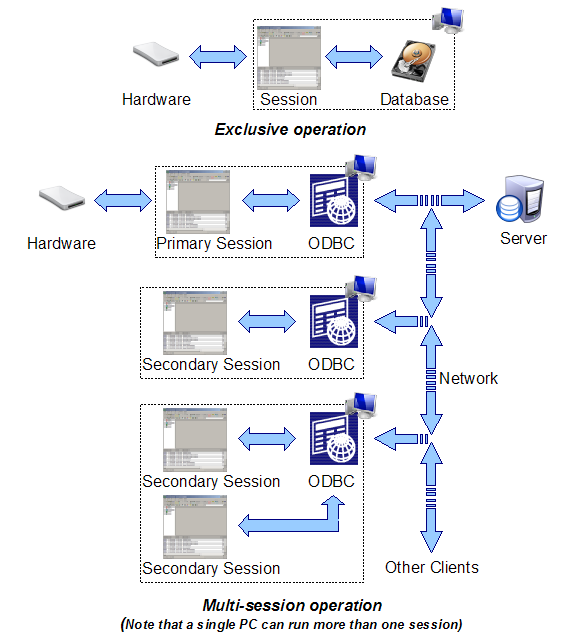 Access Manager has always supported
multiple users, but since Version 2.20 it has allowed multiple users to log in at the same
time. The former is called exclusive operation, whereas the latter is called multi-session
operation. If your requirement is only ever going to be one user viewing the database at a
time, it is recommended that you create an exclusive database as you will find it faster
and simpler to maintain (there being just one database file which is entirely maintained
by Access Manager). Multi-session operation requires the installation and use of a database server. Each Access Manager session is linked
to the database server using Open Database
Connectivity (ODBC), which provides a degree of flexibility in the choice of
database server.
Access Manager has always supported
multiple users, but since Version 2.20 it has allowed multiple users to log in at the same
time. The former is called exclusive operation, whereas the latter is called multi-session
operation. If your requirement is only ever going to be one user viewing the database at a
time, it is recommended that you create an exclusive database as you will find it faster
and simpler to maintain (there being just one database file which is entirely maintained
by Access Manager). Multi-session operation requires the installation and use of a database server. Each Access Manager session is linked
to the database server using Open Database
Connectivity (ODBC), which provides a degree of flexibility in the choice of
database server.
With an exclusive database there can only ever be one Access Manager session. It is
either online and can therefore communicate with the EasyOpen hardware, or it is offline
and cannot. When there are multiple sessions only one can be online and communicating with
the hardware, but providing there is at least one session online all the other sessions
will behave as if they communicating directly with the hardware. The only thing the other
sessions can't do is go online or offline (because they have no hardware attached to set
online or offline). The online session is the primary session, whilst all the
other sessions are secondary sessions. Note that if the hardware is connected
via a LAN or WAN, any session can become a primary session provided the PC on which it is
running has the correct drivers installed. If you want to work this way you must ensure
that the RS485 server is set up to allow one connection at a time, otherwise multiple
sessions will attempt to become the primary session and communication with the hardware
will be chaotic.
A Suggested Setup
You will probably find it simplest to have a single PC set up to run the primary
session (ie it will be the only PC with the necessary drivers), and have that PC running
the primary session all the time. Unless your database server is acting as a server for
other (critical) applications, it is best to run the primary session and the database
server on the same PC. For maximum convenience and reliability you will
probably want to run the primary session as a service.
The tag allocation reader can either be a USB-connected reader or a
controller-connected reader as normal, but tag scanning can be carried out from either the
primary session or a secondary session. The best options are either to use a USB-connected
reader attached to the PC used for tag scanning, or if using a controller-connected reader
to scan the tags using the primary session.
A database server is an application which provides database services for other
applications. There are many such applications, but Access Manager works with Firebird
Superserver (not Classic Server), MySQL, and PostgreSQL. It may work with other
backend database servers, but since they each have their own dialects this is by no means
certain.
In addition to the database server each client PC will need an appropriate ODBC driver. This often comes free with the server
(usually in a separate download), but commercial third-party drivers are available also.
Details of how to set up and maintain a database server are beyond the scope of this
Help; you should consult the relevant documentation for the server. In general you need to
be able to:
- Create, delete and edit database users.
- Create a database and set the access rights to it.
- Compact a database.
- Backup a database.
- Delete a database.
However, some helpful hints are given here which should help you get started.
Firebird
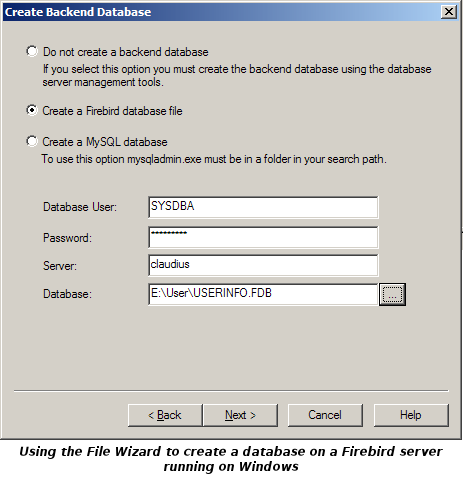 Access Manager is shipped with Firebird and is most closely integrated with
Firebird. The File Wizard (which runs when Access Manager first starts, or if you select from the menu) allows you to create a suitable new Firebird
database on any Firebird server. To do this you need to have an account on the server.
Firebird is installed with a default administrative account SYSDBA. According to
the Firebird Quick Start guide:
Access Manager is shipped with Firebird and is most closely integrated with
Firebird. The File Wizard (which runs when Access Manager first starts, or if you select from the menu) allows you to create a suitable new Firebird
database on any Firebird server. To do this you need to have an account on the server.
Firebird is installed with a default administrative account SYSDBA. According to
the Firebird Quick Start guide:
This account has all the privileges on the server and cannot be deleted.
Depending on version, OS, and architecture, the installation program will either
- install the SYSDBA user with the password masterkey (actually, masterke:
characters after the eighth are ignored), or
- ask you to enter a password during installation, or
- generate a random password and store that in the file SYSDBA.password within your
Firebird installation directory.
If the password is masterkey and your server is exposed to the Internet at all
– or even to a local network, unless you trust every user with the SYSDBA password
– you should change it immediately using the gsec command-line utility. Go to a
command shell, cd to the Firebird bin subdirectory and issue the following command to
change the password to (as an example) icuryy4me:
gsec -user sysdba -pass masterkey -mo sysdba -pw icuryy4me
Notice that you specify “sysdba” twice in the command:
- With the -user parameter you identify yourself as SYSDBA. You also provide
SYSDBA's current password in the -pass parameter.
- The -mo[dify] parameter tells gsec that you want to modify an account – which
happens to be SYSDBA again. Lastly, -pw specifies the type of modification: the password.
If all has gone well, the new password icuryy4me is now encrypted and stored, and
masterkey is no longer valid. Please be aware that unlike Firebird user names, passwords
are case-sensitive.
The Quick Start guide then goes on to tell you how to create additional database server
users.
If you need to run multiple Firebird clients on one PC, and the default client is not
the one Access Manager should be using, you should copy the correct version of
fbclient.dll to the Access Manager program folder. This is an advanced topic and further
information on running multiple server versions on one PC is beyond the scope of this
document.
MySQL
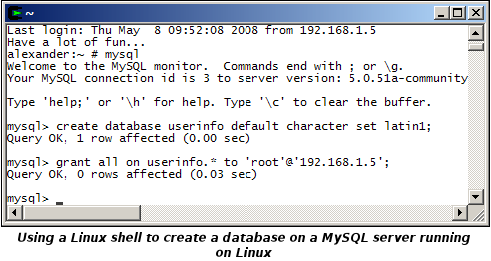 You can
create a provisional MySQL database using the mysql command line tool as follows:
You can
create a provisional MySQL database using the mysql command line tool as follows:
create database userinfo default character set latin1;
Creates a database called userinfo with Windows Western European character set.grant all on userinfo.* to 'root'@'client';
Grants all rights to all parts of database userinfo to user root.drop database userinfo;
Destroys the database called userinfo.
Note that when creating the database proper you should create at least one user with a
robust password or your database will be vulnerable to hacking.
PostgreSQL
The initial setup of PostgreSQL for Windows is integrated into the installer. There is
a lot to do but it is fairly straightforward. pgAdmin can then be used to manage the
database and users.
The initial setup of PostgreSQL for Linux is quite complicated and well beyond the
novice user, as it requires manual editing of various configuration files. Even an
experienced Linux user will need to seek out instructions on the internet. In brief you
will need to:
- Create a database administrative user (most administrators give this user the username postgres).
- As the administrative user you need to initialise the data directory using initdb.
- Edit postgresql.conf to set tcpip_socket to true.
- Edit pg_hba.conf to include the line host all all aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd 255.255.255.255
trust, where aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd is the IP address of the client PC.
- Start the server using pg_ctl (you will probably want to automate this using a
suitable entry in init.d).
- Create a database user using createuser.
- Create a database using createdb.
You will need to Vacuum the database regularly, and of course have a proper
backup strategy.
Database Server Comparison
The following information is likely to become out of date, so you are advised to check
any database server that you think meets your requirements. You will find that performance
may vary dramatically depending on the operating system and whether the server and primary
session are on the same PC or not. A newer, faster PC will not necessarily outperform an
older PC running a different operating system. To help you compare database servers, a
database speed index tool can be found under the Access Manager Help menu.
| Name |
Speed |
Encryption |
Licensing |
Platforms |
Ease of Installation |
Ease of Use |
| Firebird Superserver |
Fastest |
No |
Mozilla Public License |
Windows 32, Linux 32, Linux 64, Solaris/Sparc
32, Solaris 64. |
Easy |
Moderate |
| MySQL |
Slowest |
Yes |
GPL and Commercial |
Windows 32, Windows 64, Linux 32, Linux 64,
Solaris, FreeBSD, MacOS X, HP-UX, IBM AIX, IBM i5/OS, QNX, Netware, SCO. |
Moderate |
Moderate |
| PostgreSQL |
Medium |
Yes |
BSD |
Windows, Linux 32, Linux 64, Solaris/Sparc |
Difficult |
Difficult |
 Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a technology that allows a
database client PC to talk to a database server even if the two machines are not running
the same operating system. To a degree it also allows the client PC to talk to completely
different database server engines. Each client PC needs to run an ODBC driver suitable for
the intended database server engine. There should be no problem running multiple ODBC
drivers on a client PC if that is necessary.
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a technology that allows a
database client PC to talk to a database server even if the two machines are not running
the same operating system. To a degree it also allows the client PC to talk to completely
different database server engines. Each client PC needs to run an ODBC driver suitable for
the intended database server engine. There should be no problem running multiple ODBC
drivers on a client PC if that is necessary.
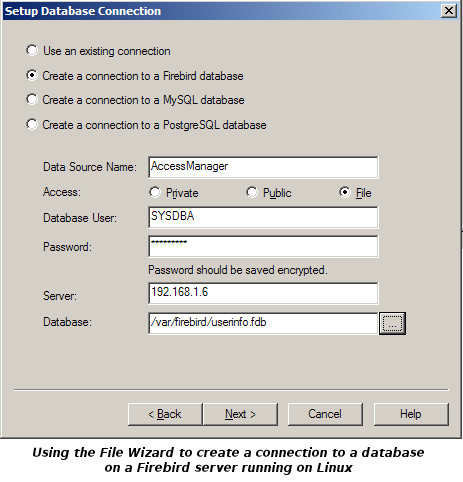
When a client PC connects to a server the ODBC driver needs to be given the details of
the connection. The Access Manager File Wizard (which runs when Access Manager first
starts, or if you select from the menu) will gather
some basic information from you and use it to create the connection details. Alternatively
you can ask the Wizard to let you use the Windows ODBC connection manager, but you will
find you will have to enter not only the basic information that the File Wizard would have
asked for, but also some rather obscure details.
The connection information is stored in one of three ways:
- Privately (Microsoft call this a user data source).
The information gathered will only be accessible to user(s) who can log in to the Windows
account under which the data was gathered. Anyone else would have to re-enter the
information. The password may or may not be saved in an encrypted form, depending on which
ODBC driver is used.
- Publicly (Microsoft call this a machine data source).
The information will be accessible to anyone who has a Windows account on the client PC.
Users on other client PCs would have to re-enter the information. The password may or may
not be saved in an encrypted form, depending on which ODBC driver is used.
- In a file (Microsoft call this a file data source).
The information will be accessible to anyone who has access to the file. This has the
great benefit that the information need only be entered once. Since this information
includes a password, Access Manager will encrypt the password before saving it in the
file, but only if you use the Wizard to gather the information. The password will not be
encrypted if you use the Windows ODBC connection manager.
Windows ODBC Connection Manager (Advanced)
If you elect to use the Windows ODBC connection manager, you will need to consult the table of data source connection settings, or your connection will be
problematic.
 Access Manager has always supported
multiple users, but since Version 2.20 it has allowed multiple users to log in at the same
time. The former is called exclusive operation, whereas the latter is called multi-session
operation. If your requirement is only ever going to be one user viewing the database at a
time, it is recommended that you create an exclusive database as you will find it faster
and simpler to maintain (there being just one database file which is entirely maintained
by Access Manager). Multi-session operation requires the installation and use of a database server. Each Access Manager session is linked
to the database server using Open Database
Connectivity (ODBC), which provides a degree of flexibility in the choice of
database server.
Access Manager has always supported
multiple users, but since Version 2.20 it has allowed multiple users to log in at the same
time. The former is called exclusive operation, whereas the latter is called multi-session
operation. If your requirement is only ever going to be one user viewing the database at a
time, it is recommended that you create an exclusive database as you will find it faster
and simpler to maintain (there being just one database file which is entirely maintained
by Access Manager). Multi-session operation requires the installation and use of a database server. Each Access Manager session is linked
to the database server using Open Database
Connectivity (ODBC), which provides a degree of flexibility in the choice of
database server. Access Manager is shipped with Firebird and is most closely integrated with
Firebird. The File Wizard (which runs when Access Manager first starts, or if you select
Access Manager is shipped with Firebird and is most closely integrated with
Firebird. The File Wizard (which runs when Access Manager first starts, or if you select  You can
create a provisional MySQL database using the mysql command line tool as follows:
You can
create a provisional MySQL database using the mysql command line tool as follows:
 Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a technology that allows a
database client PC to talk to a database server even if the two machines are not running
the same operating system. To a degree it also allows the client PC to talk to completely
different database server engines. Each client PC needs to run an ODBC driver suitable for
the intended database server engine. There should be no problem running multiple ODBC
drivers on a client PC if that is necessary.
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a technology that allows a
database client PC to talk to a database server even if the two machines are not running
the same operating system. To a degree it also allows the client PC to talk to completely
different database server engines. Each client PC needs to run an ODBC driver suitable for
the intended database server engine. There should be no problem running multiple ODBC
drivers on a client PC if that is necessary.